Plant Response Mechanisms
Hormones can initiate a response to a stimulus but the way a plant responds is called a tropism. Phototropism is a plant's response to light. When light hits a plant, certain proteins in the leaves initiate the release of auxin to one side of of plant. elongating cells on that side. As the cells on one side elongate, the plant bends.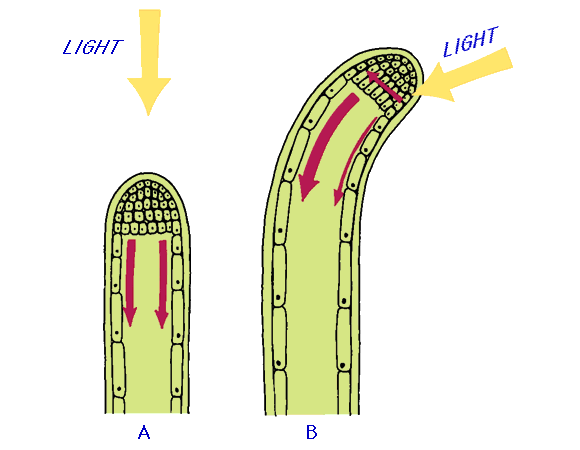 A plant can respond positively or negatively to a stimulus. The root of a seedling responds positively to gravity, which is an example of gravitropism. Scientists believe that heavy concentrations of auxin inhibit growth on one side of the root while concentrations of auxin on the other side elongate cells and stimulate growth there, causing the root to bend until it digs into the soil. Organelles called statoliths move throughout the cell, responding to gravity and influencing the concentration of auxin in the cells.
A plant can respond positively or negatively to a stimulus. The root of a seedling responds positively to gravity, which is an example of gravitropism. Scientists believe that heavy concentrations of auxin inhibit growth on one side of the root while concentrations of auxin on the other side elongate cells and stimulate growth there, causing the root to bend until it digs into the soil. Organelles called statoliths move throughout the cell, responding to gravity and influencing the concentration of auxin in the cells.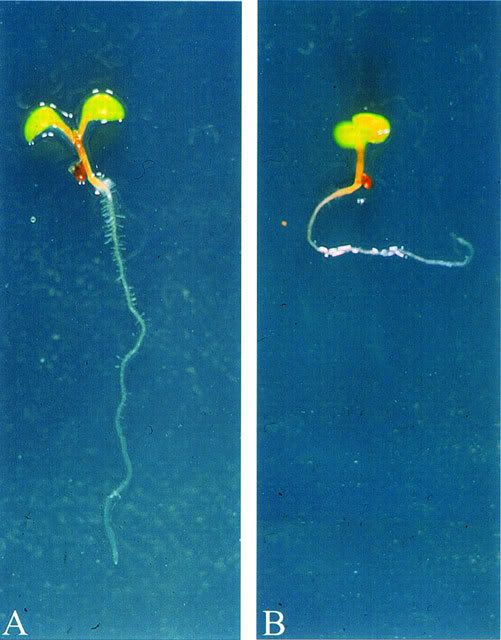 A few plants have developed the ability to respond to touch. The mimosa pudica responds by cringing, shaking and curling up. At the touch of three hairlike bristles, the Venus flytrap closes, usually ensnaring an insect for food. Scientists believe that loss of turgor pressure and immediate active transport of ions out of the cell causes the rapid movement in such plants.
A few plants have developed the ability to respond to touch. The mimosa pudica responds by cringing, shaking and curling up. At the touch of three hairlike bristles, the Venus flytrap closes, usually ensnaring an insect for food. Scientists believe that loss of turgor pressure and immediate active transport of ions out of the cell causes the rapid movement in such plants.  Plants can also respond to varying periods of light and dark. Most flowering plants have a "night clock" and flowers sprout based of the length of night. Some plants are short-day plants while other plants flower when days are longer. Flashes of light can disturb a plant's night clock. Florists manipulate this to grow flowers year round. Phytochrome is a protein located in the leaves of many plants. It is responsible for initiating flowering in plants based of the presence of light.
Plants can also respond to varying periods of light and dark. Most flowering plants have a "night clock" and flowers sprout based of the length of night. Some plants are short-day plants while other plants flower when days are longer. Flashes of light can disturb a plant's night clock. Florists manipulate this to grow flowers year round. Phytochrome is a protein located in the leaves of many plants. It is responsible for initiating flowering in plants based of the presence of light.